In new analysis, Matteo Romagnoli argues that for the electrical energy sector to decarbonize as a part of the broader inexperienced transition, regulators should liberalize markets and encourage competitors to encourage the manufacturing and adoption of recent applied sciences.
In response to the Worldwide Power Company’s World Power Outlook 2022 , world demand for electrical energy might rise by 7,000 terawatt hours by 2030. This improve can be equal to the present demand in america and the European Union mixed. To fulfill this extra demand in a sustainable means, we have to seriously change the best way we generate and provide electrical energy: a process that can inevitably require the event of recent clear power applied sciences. Fortuitously, these applied sciences are already being developed.
Sadly, some specificities of the electrical energy sector hinder the speedy improvement of clean-energy expertise in favor of a extra incremental strategy to innovation. The electrical energy market depends on capital-intensive infrastructures, and the numerous funding required to construct these infrastructures may make some market members unwilling or unable to modify their core era paradigm as radically new applied sciences emerge. As well as, the various technical elements of the electrical energy grid should work collectively in a posh and built-in system, so any new technological options should be capable of operate on this broader system. These elements, amongst others, assist to clarify why radical improvements that considerably disrupt the established order can have a tough time gaining a foothold within the electrical energy market.
To encourage the electrical energy sector to develop and undertake these new applied sciences, policymakers have to establish the fitting incentives to beat revolutionary inertia. In my analysis, I examine if liberalization of the electrical energy sector, specifically the breakup of monopolies and introduction of competitors, can induce these incentives, thus fostering the event and deployment of extra radical clean-energy applied sciences.
The tutorial literature learning the connection between regulation and innovation within the electrical energy sector has already established that liberalization of the electrical energy market was instrumental to the rise in clean-energy patents noticed during the last 30 years (see Determine 1).
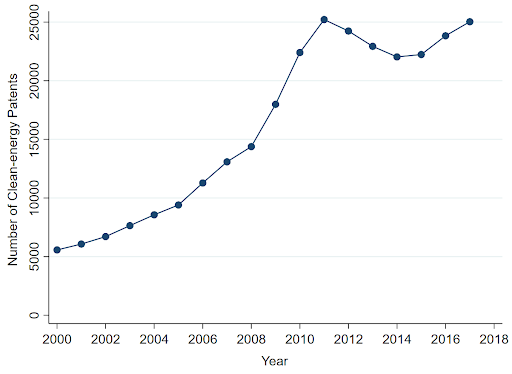
To know if additional liberalization can promote the event of extra radical clean-energy expertise (a associated however completely different query), I examined how deregulation of the electrical energy market impacts the search area of clean-energy patents. The search area is the set of information inputs and sources used to develop an invention (e.g. older patents, educational literature, databases and many others.).
The radicalness, originality, and novelty of a patent are identified to be linked to the traits of its underlying search area. A various search area makes use of information from a wide range of fields, enabling the patents’ innovators to construct on completely different strands of information and harness technological spillovers from different fields. Then again, a slim search area is characterised by information inputs from few technological fields and is related to the event of incremental improvements. Because the IEA has famous, leveraging information gathered in different technological fields can result in important advantages for clean-energy applied sciences, whereas on the similar time decreasing the necessity for added analysis and improvement spending. As an illustration, information spillovers from the manufacturing of silicon for microprocessors have performed an necessary function within the improvement of photo voltaic PV panels. Equally, petrochemical firms first achieved the event of the carbon anode now utilized in lithium-ion batteries.
The liberalization of the electrical energy market theoretically impacts the search area of unpolluted power applied sciences as a result of electrical utilities in regulated markets that curtail competitors in any other case have little incentive to develop radical clean-energy applied sciences which can be removed from their information base and will threaten their present belongings. Conversely, they’ll favor to decarbonize power provide with incremental improvements which can be extra appropriate with their present asset base and subsequently are less expensive for them to develop and undertake. The liberalization of the electrical energy market may help to interrupt this path dependency by permitting new gamers to enter the market who will not be tied to the incumbents’ core competence and era paradigm. This will finally favor a broader strategy to R&D, widening the search area of clean-energy patents and resulting in extra radical clean-energy improvements.
Determine 2 gives descriptive proof in favor of this speculation. First, the determine exhibits the common of the OECD indicator of Product Market Regulation within the electrical energy sector in nearly all OECD nations. This indicator measures the diploma of regulation within the electrical energy sector, with increased values indicating a extra regulated market. Second, the determine additionally plots the common worth of the so-called Radicalness Index for clean-energy patents developed in the identical group of OECD nations. This index, additionally computed by the OECD, measures the extent to which a patent makes use of information from “outdoors” technological fields. It’s calculated on the patent stage and may take values between zero and one, with increased values signaling that the patent makes use of extra information from outdoors technological fields.
Determine 2 suggests the existence of a unfavorable relationship between electrical energy regulation and the extent to which clean-energy applied sciences cite information from outdoors technological fields. Because the electrical energy markets of OECD nations turn out to be extra liberalized, the common worth of the Radicalness Index for clean-energy applied sciences developed in nations will increase considerably. As well as, as soon as electrical energy liberalization slows down, the Radicalness Index additionally stops rising.
Nonetheless, there could have been different elements that contributed to the event of clean-energy applied sciences alongside liberalization as seen in Determine 2. To this finish, I used knowledge on patent purposes filed over the interval 1990-2017 and relied on an instrumental variable strategy to isolate the impression of liberalization on innovation from different potential elements. Ultimately, I discovered that what we observe is certainly a causal relationship: liberalization of the electrical energy market results in clean-energy patents that cite extra from outdoors technological fields, i.e. clean-energy patents that harness extra information spillovers from different technological fields.
It’s important that policymakers perceive how electrical energy regulation can contribute to the event of higher clean-energy improvements. Adjustments to the design and regulation of the electrical energy sector are presently being mentioned in lots of markets around the globe. Nonetheless, among the concepts proposed and mentioned have the potential to considerably hinder competitors available in the market. (For a dialogue on this subject targeted on the European Union, see ACER 2022). In flip, decreased competitors threatens innovators’ incentives to broaden patent search areas to provide the novel applied sciences needed for decarbonizing electrical era.
Stressing the significance of a aggressive electrical energy marketplace for clean-energy innovation doesn’t imply ignoring the important thing function that the state ought to play on this market and in supporting clean-energy applied sciences. Actually, in a liberalized electrical energy market, environmental insurance policies turn out to be much more necessary, because it has been proven that these insurance policies are more practical as soon as the electrical energy market is opened to competitors. Furthermore, whereas the function of the regulator modifications within the transition from a monopoly to a aggressive electrical energy market, it doesn’t turn out to be marginal. A well-functioning electrical energy market is a prerequisite for incentivizing investments in electrical energy provide, and this can’t be achieved and not using a regulator to supervise transactions available in the market and be certain that the market features successfully. Lastly, even in a liberalized electrical energy market, public R&D is a vital lever for technological progress, because the case of the French Different Energies and Atomic Power Fee exhibits.
Liberalization of the electrical energy market is subsequently an necessary piece of the puzzle to decarbonize electrical energy provide, nevertheless it stays solely a single piece of the border puzzle that we have to clear up.
Articles symbolize the opinions of their writers, not essentially these of the College of Chicago, the Sales space College of Enterprise, or its school.
Originally posted 2023-04-03 10:00:00.